Hair loss affects many men as they age. It’s a common issue that can impact self-esteem and confidence. The good news is there are treatments available to help slow or even reverse balding in some cases.
Effective hair loss treatments for men include medications like finasteride and minoxidil, as well as hair transplant surgery. These options can help stimulate hair growth and prevent further loss. Some men also try natural remedies like scalp massage or dietary changes.
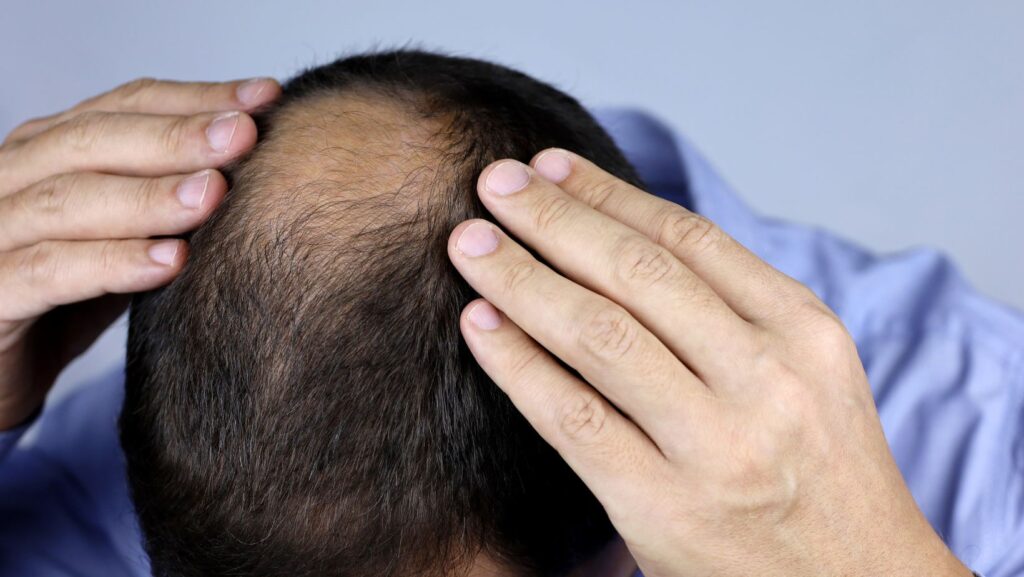
Male pattern baldness is the most common type of hair loss in men. It typically starts with a receding hairline or thinning at the crown. Genetics play a big role, but other factors like stress and diet can contribute too. Understanding the cause is key to finding the right treatment approach.
Understanding Hair Loss in Men
Male hair loss is a common condition affecting many men. It can occur due to various factors and manifest in different patterns. Early recognition of hair loss signs helps in seeking timely treatment.
Causes of Male Pattern Baldness
Male pattern baldness, or androgenetic alopecia, is the most common type of hair loss in men. Genetics play a big role in this condition. Men inherit genes that make their hair follicles sensitive to DHT, a hormone derived from testosterone. These sensitive follicles shrink over time, leading to thinner hair and eventual baldness.
Age is another factor. As men get older, their risk of hair loss increases. Some medical conditions can also cause hair loss. These include thyroid problems, iron deficiency, and autoimmune diseases.
Stress, poor nutrition, and certain medications may contribute to hair loss as well. However, these factors often cause temporary shedding rather than permanent balding.
Types of Hair Loss
Male pattern baldness is the most widespread form of hair loss. It typically starts with a receding hairline or thinning at the crown. Over time, it can progress to partial or complete baldness.
Alopecia areata is another type of hair loss. It causes round, smooth patches of baldness on the scalp or other parts of the body. This condition is believed to be an autoimmune disorder.
Telogen effluvium involves sudden, widespread hair shedding. It often occurs after severe stress, illness, or major life changes. Anagen effluvium is rapid hair loss caused by medical treatments like chemotherapy.
Tinea capitis, a fungal infection of the scalp, can also lead to hair loss. It’s more common in children but can affect adults too.
Identifying Male Hair Loss
Spotting the signs of hair loss early can help in managing the condition. A receding hairline is often the first noticeable sign. The hairline may form an M-shape as it recedes at the temples.
Thinning at the crown is another common sign. Men might notice their scalp becoming more visible through their hair. This thinning can spread and join with a receding hairline, forming a U-shape around the sides of the head.
Excessive hair shedding is also a red flag. While it’s normal to lose some hair daily, finding large amounts on your pillow or in the shower drain may indicate a problem. A doctor can perform tests to diagnose the cause of hair loss and recommend appropriate treatments.
Conventional Treatments
Men facing hair loss have several proven options to slow or reverse balding. These range from over-the-counter products to medical procedures.
Topical Treatments
Minoxidil is a common non-prescription treatment for male pattern baldness. It comes as a liquid or foam applied to the scalp twice daily. Minoxidil works by increasing blood flow to hair follicles. This helps existing hairs grow thicker and stimulates new growth.

Rogaine is the best-known brand of minoxidil. It’s available in 2% and 5% strengths. The 5% version is more effective for men. Results typically appear after 4-6 months of regular use.
Some men use ketoconazole shampoo to fight hair loss. This antifungal medication may help by reducing inflammation on the scalp.
Prescription Medications
Finasteride is an FDA-approved pill for male pattern baldness. It works by blocking DHT, a hormone linked to hair loss. Men take 1mg daily. Most see results in 3-6 months.
Propecia is the brand name for finasteride. It requires a prescription from a doctor. Side effects are rare but can include sexual problems.
Dutasteride is similar to finasteride but more potent. It’s not FDA-approved for hair loss but some doctors prescribe it off-label. The brand name is Avodart.
Some men explore prescription-based solutions like those offered by HappyHead as part of a broader approach to managing hair loss.
Surgical Options
Hair transplant surgery moves hair from thicker areas to balding spots. A surgeon removes small plugs of skin with healthy hairs. These are then placed in thinning areas.
Modern techniques create a natural look. But transplants can be costly and require multiple sessions. They work best for men with stable hair loss patterns.
Scalp reduction is another surgical option. It removes bald areas of scalp and stretches hair-bearing skin. This method is less common now due to scarring risks.
Alternative Therapies and Supportive Care
Some men explore non-medical approaches to manage hair loss. These methods focus on natural remedies, diet changes, and hair care techniques.
Natural and Herbal Remedies
Certain plant-based treatments may help with hair growth. Rosemary oil can boost hair density when applied to the scalp. Some men use saw palmetto to block DHT, a hormone linked to hair loss. Scalp massage might increase blood flow to hair follicles.
Laser therapy is another option. It uses low-level light to stimulate hair growth. This treatment can be done at home or in a clinic. Results vary from person to person.
Biotin, a B vitamin, is often taken as a supplement. It helps make hair proteins. But there’s limited proof it stops balding in men with normal biotin levels.
Nutrition and Diet
A balanced diet plays a key role in hair health. Eating the right foods can support hair growth. Iron, protein, and omega-3 fatty acids are important for strong hair.
Some men may have nutritional gaps that affect their hair. A doctor can test for these issues. Fixing deficiencies through diet or supplements may help.
Key vitamins for hair include A, C, D, and E. Zinc and selenium are also vital minerals. Eating a variety of fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins can provide these nutrients.
Hair Care and Hairstyling Tips
Gentle hair care can prevent further damage to thinning hair. Men should avoid harsh shampoos and hot water. Pat hair dry instead of rubbing with a towel.
Some hairstyles can make thinning less noticeable. Shorter cuts often work well. They can give the look of thicker hair. A skilled stylist can suggest flattering options.
For more coverage, some men choose hairpieces or wigs. These come in many styles and colors. High-quality options can look very natural. Hair extensions are another way to add volume, though they work best for longer hair. Nano hair extensions are a great option for men with longer hair, offering a lightweight and discreet way to achieve a fuller, more natural look.
Psychological Impacts of Hair Loss
Hair loss can take a toll on men’s mental health. Many guys feel less confident and attractive when they start balding. This can lead to lower self-esteem and negative body image.
Some men become depressed or anxious about their changing looks. They may avoid social situations or hide their hair loss with hats. Dating and relationships can feel more challenging too.
Hair loss can make men feel older than they are. They might worry about seeming less virile or masculine. These thoughts can affect work and personal life.
Support groups can help men cope with hair loss. Talking to others facing similar issues often provides comfort. It shows guys they’re not alone in their struggles.
Therapy is another good option for dealing with hair-related distress. A counselor can teach healthy ways to boost self-image. They can also treat any depression linked to balding.
Some men find that hair restoration treatments improve their mood. Even small changes in appearance can have big impacts on confidence. But it’s important to have realistic expectations.
Accepting hair loss is key for mental well-being. Many guys learn to embrace their new look over time. Focusing on other positive traits helps build self-esteem.
